
We hope that each of you, our wonderful readers, will thoroughly enjoy and appreciate this article we present about these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks. It was certainly our sincere pleasure to compile the information for you. May it provide you with both education and increased awareness.
While amazing, these few species listed herein represent only a portion of the natural wonders found throughout the region, though. Yet, it’s our belief that they serve as excellent representations of the wonders found here. Check out some of our many other articles for similar marvels.
Oceanic whitetip shark

Oceanic whitetip shark Facts
- Leading off this article about these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks we present the amazing creature understandably named the Oceanic whitetip shark.
- This majestic yet dangerous predator of the depths most frequently goes by the common name used here due to its appearance. Yet, the fascinating animal also holds several less often used titles. These include such terms as nigano shark, brown shark, and simply whitetip shark.
- Within the scientific community, however, it’s perhaps much better known by its formal moniker. But that’s an extremely hard name to pronounce for the layperson. That’s because this marvel of nature bears the complex technical title of the Carcharhinus longimanus.
- A degree of controversy persists inside the halls of science, though, concerning that specific appellation. The first known formal description of the fish occurred in 1831, due to the work of the French naturalist, René-Primevère Lesson, who gave it a somewhat similar name.
- The next description of the fish, however, took place in the year 1861, at the hands of the Cuban zoologist, Felipe Poey. He also provided it with a similar yet different moniker. Given this confusion, and still many others, the name used here is generally the most accepted.
- Sadly, the population of the remarkable Oceanic whitetip shark measures quite small. It also appears to be continuing to diminish at an alarming rate. That state apparently holds true throughout its range. The IUCN thus currently lists the fish as Critically Endangered.
- It faces numerous threats to its continued existence. Most of these stem from the actions of man. These include such various factors as being actively fished for its meat and fins. The creature also now faces the dual dangers posed by habitat loss and ongoing climate change.
Oceanic whitetip shark Physical Description
The mesmerizing Oceanic whitetip shark immediately captivates many fortunate enough to encounter the animal in its native environment. Unlike some species, though, it does so for several reasons. That’s due to the fact that it’s visually impressive due to both its appearance and size.
In that respect, the shark clearly follows a pattern common among many of its relatives. That’s true since it displays a certain degree of the physiological characteristic known as sexual dimorphism. In its specific case, though, this trait manifests itself purely in terms of physical measurements.
More precisely, the female of the species attains a slightly greater overall size than her male counterparts. This gender of the intriguing fish reaches an average body length of roughly 12.8 ft (3.9 m). These individuals further grow to an average body mass equaling 374.8 lb (170 kg).
Males of the creature, however, only attain an average length of body measuring about 9.8 ft (3 m). They do tend to have a slightly stockier build than the females, though. Due to this general development, their body mass is an only slightly lighter average of about 368 lb (167 kg).
In terms of overall appearance, other than this, however, both sexes of the Oceanic whitetip shark remain virtually indistinguishable at a quick glance. The upper body of the fish typically displays a gray-bronze shade. Its lower body, though, generally manifests a somewhat off-white shade.
Yet it’s the fins of the awesome animal that serve as the source of the common name. Most of these display a bright white tip. Each fish also presents a mottled pattern among adults, and black in younger specimens. A patch resembling a saddle somtimes appears between two dorsal fins.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Carcharhinidae
- Genus: Carcharhinus
- Species: C. longimanus
Oceanic whitetip shark Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
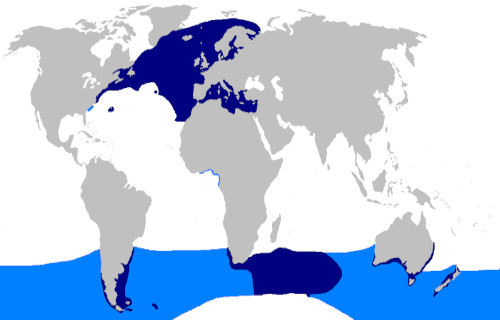
The fascinating Oceanic whitetip shark evolved as native to an extremely broad swathe of the surface of the globe. The full extent of that zone of habitation might surprise some people, though. That’s because this wonder of evolution lives in oceans worldwide between latitudes 45 N and 43 S.
The vast majority of this range of appearance consists of relatively to extremely deep waters. The creature also displays decided preferences for the temperature of the waters it lives in, as well. It also seems to favor temperatures above 68F (20C), and up to approximately 82F (28C).
Yet the fish also shows some moderate flexibility in this regard. That’s true since a certain percentage of observed specimens appeared in waters having a temperature equaling about 59F (15C). The animal does, however, seem to studiously attempt to avoid temperatures lower than this.
Despite mainly living in regions of great depths, though, it spends most of its time in the upper layers of the ocean. Most sightings occur at depths of no greater than 490 ft (150 m). Though most spotted individuals remain offshore, some do venture into areas as shallow as 120 ft (37 m).
The beautiful Oceanic whitetip shark typically lives a primarily solitary life, like many. Small, temporary groups do sometimes form, however, for hunting and feeding purposes. The animal also evolved as an active hunter, swimming and seeking out prey by both day and night equally.
As a general principle, the fish usually feeds on an impressive variety of cephalopods, like small squid, and bony fish, such as oarfish and barracuda. Yet it sometimes varies this, adopting a more flexible diet. At these times, it eats such prey as stingrays, birds, crustaceans, and sea turtles.
Porbeagle
Porbeagle Facts
- Next up in this compendium of 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks comes the bewildering animal man knows simply as the Porbeagle.
- The short term given it here serves as the most frequently used common name for this didtinctive fish. It’s actually a species of what’s known as mackerel sharks. However, the intriguing Lamnidae also goes by several other names, in various parts of its natural range.
- These alternate appellations include such names as the Beaumaris shark, Atlantic mackerel shark, bottle-nosed shark, and blue dog. Professionals, though, such as researchers, tend to employ its formal name when referring to it. That’s the relatively simple term Lamna nasus.
- It received that designation due to the work of the French naturalist, Abbé Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre. He accomplished the first official acknowledgement of the creature as a separate and distinct species. This scientifically noteworthy event occurred in the year 1788.
- Regardless of the term one chooses to use to refer to it, though, the shark remains a fascinating animal. It’s also known for being quite fast, and highly active. Yet it’s well-known as comparatively docile. Only a handful of bites by this species have been reported, none serious.
- Sadly, however, the population of the amazing Porbeagle continues to drop sharply. Though the wonder now enjoys a measure of protection, this applies in only a few areas. Various nations and Unions now ban hunting, but this only applies within their own area of influence.
- The remarkable fish therefore faces numerous threats. These obviously include commercial fishing, as well as sport fishing. Climate change also now poses a danger to it. For all these reasons, the IUCN now lists the species as Vulnerable on its Red List of Threatened Species.
Porbeagle Physical Description
The physique of the remarkable Porbeagle quickly impresses those few individuals fortunate enough to encounter it. It’s worth noting, however, that it does so for attributes wholly unrelated to sheer size. That’s because this variety of shark only ranks as slightly above average in that regard.
Although populations vary somewhat in number, largely depending on their region, in many of these one trait prominently stands out. That’s due to the fact that some populations display the physiological characteristic of sexual dimorphism. In its case, though, this manifests in sheer size.
More specifically, females of the species attain a moderately greater mean length than their male counterparts. As a result of this size disparity, the females reach an average body length of approximately 9.8 ft (3.0 m). Males, meanwhile, only average roughly 8.2 ft (2.5 m) in overall length.
Despite the highly notable difference in length, though, average weights measure among them about the same. Most specimens only weigh around 298 lb (135 kg). Exceptional individuals do occur, however. The heaviest known member of the amazing species weighed in at 510 lb (230 kg).
Its overall body shape’s often referred to as comparatively stout, with males being somewhat more so than females. The elongated snout tapers to a pointed structure. Its eyes further develop as large, and deep black in color. Its mouth also develops as proportionately quite large and curved.
In terms of general coloring, though, the interestig Porbeagle displays a fairly common pattern. The upper surface dislays as a moderate to dark gray color. Its underside, meanwhile, typically shows an off white shade. Some populations also display irregular, dusky blotches across the belly.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Lamniformes
- Family: Lamnidae
- Genus: Lamna
- Species: L. nasus
Porbeagle Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
One factor working in the favor of the amazing Porbeagle is its natural distribution. That’s because this marvel of Nature has an extremely broad, yet simultaneously specific, range of habitation. It evolved to possess what ichthyologists, scientists who study fish, call an amphitemperate range.
That’s simply a technical term that means three certain specific things. Firstly, the animal appears almost globally, within certain parameters. Secondly, however, those very same parameters restrict it to the temperate waters of both hemispheres. Finally, its entirely absent from tropical areas.
Within that zone of habitation, though, it inhabits a relatively broad range of depths. In this, different populations present varying preferences. Thus, some groupings appear offshore, at depths of as much as 4,460 ft (1,360 m). Others, meanwhile, appear at depths as shallow as 3.3 ft (1m)!
Yet, in all marine regions of the world this wonder of Nature makes its home in, some individuals display a daily migration pattern, while others do not. Those specimens that migrate usually spend the majority of the day at greater depths. These then later move toward the surface at night.
The remarkably intriguing Porbeagle appears either in small groups or singly. In both instances, it’s also one of the few known fish species to exhibit signs of play. That’s due to the fact that, on some occasions, individuals wrap themselves in rolling and unrolling themselves in kelp strands.
Like other sharks, it also evolved as an actively predatory creature. It’s extremely opportunistic, as well, feeding on virtually any small or medium-sized bony fish it finds. Small cephalopds, especially squid, additionally form an important part of its diet. Lifespan ranges from 30-40 years.
Scalloped Hammerhead
Scalloped Hammerhead Facts
- Our next choice for inclusion in this gathering of these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks is the intriguing denizen of the depths named the Scalloped Hammerhead.
- The attention-grabbing name we’ve used herein serves as the most frequently used common name for this astonishing fish. The marvel’s also known by several other titles, though. Those include terms such as the kinky-headed shark, bronze, and southern hammerhead.
- Within scientific circles, though, the creature’s perhaps better known by its purely formal moniker. Fortunately for the layperson, though, that’s a simpler term than many of its relatives hold. That’s because it bears the official name in the annals of science of Sphyrna lewini.
- It received that technical name due to the efforts of the team of Edward Griffith and Charles Hamilton Smith. The highly respected pair of British naturalists accomplished the first formal acknowledgement of it as a separate and distinct species. This occurred in the year 1834.
- The two individuals originally gave it another, different title, however. Before changing it to the term it’s known by now, the pair at first titled it Zygaena lewini. Regardless of which name one chooses to use when referring to it, the shark remains a truly impressive fish species.
- Sadly, however, the population of the remarkable Scalloped Hammerhead presently appears to be in stark decline. This unfortunate trend also seems to hold true throughout the entirety of its known range. The IUCN therefore currently lists it as Critically Endangered on its Red List.
- The amazing fish faces many threats to its continued existence. Previously, this mostly consisted of overfishing, as it was hunted in some regions. Due to its fragile population numbers now, though, it likely faces its greatest danger going forward from climate change.
Scalloped Hammerhead Physical Description
The remarkable Scalloped Hammerhead fascinates most of those fortunate enough to encounter it. Unlike some of its kindred, though, it does so for more than one reason. In this intriguing species, Nature created a true masterpiece that continues to tantalize many researchers even today.
The intriguing species grows to highly respectable physical measurements. It also follows the pattern common among most of its relatives, though, regarding that statistic. That’s true since the animal displays a moderately large degree of the physiological characteristic of sexual dimorphism.
Although the genders present the same general appearance, the size varies significantly between them. More precisely, females of the species typically attain a much greater size than their male counterparts. That’s a trend common among most known species of shark around the world.
The females attain an average body length measuring roughly 8.2 ft (2.5 m). They’re surprisingly light, however. Most of this sex average 80 lb (36.2 kg) in weight. Exceptional individuals do occur, of course. But even these rarely exceed these measurements by any significant degree.
Males of the Scalloped Hammerhead, however, usually remain much smaller in both categories. Body length averages 4.9 – 5.9 ft (1.5 – 1.8 m). They’re body mass ranks appropriately smaller as well. This equals 64 lb (29 kg). The largest specimen on record measured 14 ft (4.3 m) in length.
In overall appearance, though, the two sexes remain virtually indistinguishable. The coloring of the remarkable creature generally consists of varying shades of light gray. Its’ most distinctive feature, though, is obvious. That’s the large hammer-shaped head, thus the primary common name.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Sphyrnidae
- Genus: Sphyrna
- Species: S. lewini
Scalloped Hammerhead Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The remarkable Scalloped Hammerhead evolved as native to a relatively broad swathe of the marine areas of the globe. The general area, however, likely won’t surprise many people. That’s becasue it evolved as endemic to the section of the oceans that ranges from roughly 46°N to 36°S.
Within that widespread zone of habitation, though, certain areas see greater numbers. These principle regions include the waters off South Africa and Japan. Other zones of concentration include the Indian Ocean, Red Sea, and the warm waters of Hawaii, Tahiti, and Australia.
Inside of that range, however, the impressive animal displays decided and highly specific preferences regarding its choice of habitat. In all areas the shark inhabits, it primarily lives near the coast. It’s most frequently sighted either over or comparatively near the continental shelves.
The marvel of Nature also appears only in either warmer temperate or tropical waters. It’s not a deep-diving species, by any means. A maximum observed depth for the species only equals 3,400 ft (1.03 km). Most often, however, individuals spend their time above depths of 82 ft (25 m).
The Scalloped Hammerhead typically lives in relatively large groups, called schools. Unlike many other related creatures, though, it remains active at all times of the day and night. Compared to some of its many relatives, they’re considered relatively docile in their behavior patterns.
Like all sharks, the wonder evolved as a fully carnivorous species. It principally feeds on prey such as various small fish, octopi, and squid. It’s also an opportunistic hunter, feeding on whatever prey’s locally available. In turn, its own predators mainly consist of larger varieties of sharks.
Great White Shark

Great White Shark Facts
- Appearing here in this listing of 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks we give you the renowned marvel of the seas named the Great White Shark.
- The term it’s generally known by serves as one of the common names for a truly incredible variety of mackerel shark. This marvel of Nature and evolution also goes by multiple other general names, though, such as the great white, the white shark, and white pointer.
- Unfortunately fo the layperson, the animal also has the somewhat tongue-twisting scientific name of Carcharodon carcharias. But, no matter what name one uses to refer to it, this magnficent creature unquestionably represents one of the oceans primary apex predators.
- The remarkable creature received that hard to pronounce technical title due to the efforts of Carl Linnaeus. The esteemed Swedish researcher accomplished the first recognition of it as a separate and distinct species. He achieved that scientifically noteworthy feat in 1758.
- This incredibly efficient marine hunter also has almost no known natural predators of its own. This holds true throughout the entirety of its natural range. The rare exception, though, would be extremely uncommon attacks by orcas when other, easier prey cannot be found.
- The breathtaking Great White Shark also exemplifies the ideal example of a very fast and far-ranging hunter. This true marvel of Nature evolved the ability to reach speeds measuring as much as 35 mph (56 kph). It can also safely dive to depths of as deep as 3,900 ft (1,200 m).
- For a variety of reasons, the IUCN lists this majestic creature as Vulnerable on its published Red List. This holds true largely due to such factors as habitat loss and reduction of its prey, due to human commercial fishing practices. However, it also faces danger from climate change.

Great White Shark Physical Description
The astonishing Great White Shark instantly captures the attention of those individuals fortunate enough to encounter one. Indeed, its various attributes combine to make it one of the most recognizable shark species on the planet. This occurs due to both its outward appearance and size.
It also follows a natural pattern quite common among its many kindred around the world in this respect. That’s in the fact that it displays a certain degree of the physiologicial characteristic of sexual dimorphism. In its specific case, this trait mainly manifests itself in terms of dimensions.
Specifically, females of the species attain greater average measurements in both length and weight than their male counterparts. For that gender, individuals remain capable of reaching 21 ft (6.4 m) long. These same examples also sometimes achieve masses of 5,000 lb (2,270 kg) or more.
Males, meanwhile, do not typically achieve so grand a size. They generally average somewhere between 13 – 16 ft (4 -5 m) in length. Weights usually remain accordingly less, with a mean ranging from 1,100 – 2,400 lb (500 – 1,100 kg). Exceptions, though, sometimes reach 4,000 lb (1,800 kg).
The overall body design of both sexes evolved as approximately the same, very often being compared to that of a modern torpedo. That of the male, however, often develops as slightly more stout in form. The snout of the marvelous fish typically possesses a pronounced conical shape.
Yet, it’s the distinctive coloring of the aptly-named Great White Shark that usually draws the most interest from observers. The upper body typically shows dark gray or blue-gray, camouflaging it when from above. Its underside, though, displays white, concealing it when viewed from below.
The marvel of Nature also boasts many other features, as well. These include fins located on its back, sides, and tail. The fish also has several rows of teeth, numbering up to 300 in total. Its eyes develop as large and deep black, and it has gills positioned on each side of the large head.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Lamniformes
- Family: Lamnidae
- Genus: Carcharodon
- Species: C. carcharias
Great White Shark Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
It bears mentioning that the remarkable Great White Shark possesses many more advantages than just its purely physical attributes. That holds true because the astonishing animal also has an almost global range of habitation. This gives it that decided advantage over numerous other species.
To the great amazement of many who learn of it, this truly amazing predatory fish inhabits virtually all regions of temperate and tropical waters. But, the greatest known concentration of its present numbers presently occurs in the waters off the coast of the country of South Africa, in Africa.
The incredibly powerful hunter most commonly appears in coastal and offshore areas. This practice, unfortunately, also frequently leads to encounters with humans. There, this denizen of the deep rarely, though certainly not never, enters waters with depths of less than 1,000 ft (305 m).
This extremely dangerous creature much more commonly appears at vastly more significant depths, however. These often reach as deep as 3,900 ft (1,200 m). Wherever it appears, though, the marvel of Nature demonstrates that it generally prefers to stalk a moderately large, regular territory.
Given its devastating power and surprising speed, the supremely effective predator of earth’s marine regions understandably feeds on a wide variety of prey. In point of fact, this monstrously powerful, and also highly aggressive, hunter actively feeds on virtually any creature it can find and catch.
The awesome Great White Shark nevertheless does tend to display certain preferences for its choice of prey, as nearly all living creatures do. Detailed observations indicate that these favorites include tuna, dolphins, seals, sea turtles, sea otters, and even, when possible, various marine birds.
Spiny Dogfish
Spiny Dogfish Facts
- Here, in this grouping of these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks, we give you the interesting animal given the name of the Spiny Dogfish.
- The quite evocative term we’re using for it perfectly serves as one of the common names for one of the best known members of the Squalidae Family of sharks. The truly remarkable marine animal also remains known by a very large number of other alternate names, though.
- These several synonymous titles include such equally distinctive names as the mud shark, the spurdog, and the piked dogfish, just to name a few of them. Among professional researchers, though, the amazing creature bears the difficult scientific name of the Squalus acanthias.
- The creature received that specific moniker due to the efforts of Carl Linnaeus himself. The highly esteemed Swedish zoologist recorded the first offical recognition of it as a separate and distinct species. He accomplished that scientifically noteworthy deed in the year 1758.
- Unfortunately, its situation appears to be somewhat unstable in many respects. Due to its population status, as well as numerous other factors, the IUCN currently lists it as Vulnerable. This lamentable status appears on the organization’s published Red List of Threatened Species.
- The multiple and varied dangers facing the remarkable evolved Spiny Dogfish continue to rapidly escalate, regrettably. Among these perils, over fishing continues to be the greatest threat to its continued existence, since the shark constitutes a commercially fished species.
- Other, newer factors also now pose serious, potentially terminal threats to this amazing species, though. Habitat loss, due to the various actions of man threaten to greatly reduce its range. The ongoing effects of climate change also now pose a great danger for it.
Spiny Dogfish Physical Description
It bears noting that, while remarkably impressive in many ways, sheer size isn’t the strong suit of the amazing Spiny Dogfish. To the great surprise of many people, this marvel of Nature actually remains a very small example of its Order, the Squaliformes. It’s nonetheless still quite impressive.
The species does, however, display a respectable degree of the physiological characteristic known as sexual dimorphism. In the case of this particular representative of its kind, this evolutionary trait typically manifests itself in terms of size, with females being slightly larger in average length.
Although exceptional individuals do exist, of course, adult males attain an average body length only equaling approximately 39 in (1 m). Mature females of this fascinating variety of shark, on the other hand, greatly exceed this, reaching an average length measuring roughly 62.6 in (1.59 m).
Otherwise, both genders strongly resemble each other in appearance, presenting the same basic color pattern. Members of both sexes display an overall grayish-brown shade, with the upper half of the body being a darker shade. Meanwhile, the underside usually remains much lighter in color.
It’s the surprising presence of one particular physical feature, though, that gives the Spiny Dogfish its unique common name. That’s the existence of two very sharp spines that appear on the dorsal area, which the resourceful animal uses as a means of self-defense when it’s threatened.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Squaliformes
- Family: Squalidae
- Genus: Squalus
- Species: S. acanthias
Spiny Dogfish Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
To the great surprise of some people, the remarkable Spiny Dogfish inhabits a comparatively wide range of the marine waters of the world. Populations of this fascinating fish inhabit many varied regions. This includes the Pacific, the Atlantic, and also portions of the Indian Ocean.
In whatever part of the world populations of the animal appear, however, all individuals share one special trait. That’s because all of them maintain the same basic pattern of behavior regarding choice of habitat. More precisely, this animal evolved to live primarily as a bottom-dwelling species.
With that being said, though, some specimens of this intriguing type of shark have been observed by researchers at depths of as much as 2,300 ft (700 m). The great majority of observed groupings or individuals nevertheless make their home at depths of between 160 – 490 ft (50 – 149 m).
Like all other known sharks, the tantalizing Spiny Dogfish feeds entirely as an aggressive carnivore. Despite its comparatively small size, however, this animal is certainly no exception to this trait. It actively hunts a wide variety of prey, including fish, squid, shrimp, crabs, and even jellyfish.
Though some monitored examples travel singly, the vast majority of members of this intriguing species appear in incredibly large packs, that can number in the thousands. After mating, live birth occurs an average of an astonishing 22 – 24 months later. A typical lifespan averages 35 – 54 years.
Bonnethead Shark
Bonnethead Shark Facts
- Next up in this compilation of 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks is the unique creature of the oceans of the world bearing the moniker of the Bonnethead Shark.
- This highly distinctive term easily serves as the most frequently used of several common names for this fascinating marine creature. The true biological wonder also goes by the somewhat inventive alternate name of the shovelhead, as well as that of the bonnet shark.
- The scientific name for it, meanwhile, remains comparatively simple, as such technical terms go. That’s because the large fish bears the official name of the Sphyrna tiburo. By either of these terms, though, it represents yet another impressive variety of hammerhead shark.
- The first known scientific recognition of it as a separate and distinct species took place long ago. More specifically, that noteworthy event happened in the year 1758. That further resulted from the research of the renowned Swedish zoologist and botanist, Carl Linnaeus.
- Its known population appears to be relatively stable in only certain limited portions of its range. Regrettably, the amazing Bonnethead Shark appears to be suffering from significantly reduced numbers in other regions, however. It’s been heavily targeted in fishing practices.
- This unfortunate fact further holds true in several portions of its natural range. Due to this overall decline, the IUCN now lists the marvelously evolved marine species as Endangered. This lamentable status is reflected in the organization’s Red List of Threatened Species.
- This single species accounts for as much as half of all shark catches in its range. The intriguing fish also suffers from other dangers as well. Habitat degradation and outright loss form an obvious threat, of course. Nevertheless, climate change must also now be considered a threat.
Bonnethead Shark Physical Description
The fascinating Bonnethead Shark impresses those individuals who learn of its existence for reasons other that sheer size. That’s due to the simple fact that it’s a fairly small species. In point of fact, this marvel of Nature forms the smallest of all currently known varieties of hammerhead shark.
The fascinating creature also displays only a slight degree of the physiological characteristic known as sexual dimorphism. In this specific instance, that trait manifests itself in terms of physical size. More precisely, the females of the species tend to attain slightly greater lengths than the males.
Overall, however, individual examples of this variety of hammerhead shark reach an average body length measuring roughly 2 – 3 ft (0.61 – 0.91 m). Exceptional specimens do naturally occur, though. Due to this, the largest example measured to date reached approximately 5 ft (1.5 m) in length.
Most frequently, the upper portion of the body of the captivating Bonnethead Shark presents a dull grayish-brown color to the observer. The underside, meanwhile, usually develops as markedly lighter in coloring. It also develops a smooth, broad, shovel-like head, hence the common name.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Sphyrnidae
- Genus: Sphyrna
- Species: S. tiburo
Bonnethead Shark Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The incredible Bonnethead Shark inhabits a relatively small portion of the marine regions of the world. Not only that, but its range also happens to be highly specialized in nature. That’s because, throughout its entire range, it only appears in a comparatively narrow strip along the shoreline.
More precisely, it primarily appears along the east and west coasts of the United States, in North America. To the east, however, individuals live as far south as the Gulf of Mexico and Brazil, in South America. The northern part of its zone of habitation reaches as far as New England.
In the west, meanwhile, a few reported populations appear as far south as the waters near the country of Ecuador, in South America. To the north, in the Pacific Ocean, though, this shark makes appearances as far up the coast as southern California. Groupings further appear sporadically.
This species also migrates comparatively long distances with the seasons in both parts of its range. As a result of this, individuals generally move southward as the water temperature changes. This shark typically prefers to inhabit regions with water temperatures reaching over 70 F (21 C).
This marvel of Naure and evolution also displays a fondness for specific types of habitat. These mainly include seagrass, areas with very muddy or sandy bottoms. It also, however, sometimes lives in shallow bays and estuaries. In these regions, though, it prefers the presence of seagrass.
Most commonly, the Bonnethead Shark travels in moderately small groups. These generally number no more than 1 individual, except during migrations. At this time, they may be found in groups of hundreds or occasionally even thousands. Females usually prefer very shallow water for birthing.
This species stands apart from all other known sharks in one surprising way. This occurs despite being the smallest of its kind, proving Nature has no care for such matters. That’s because all other sharks feed entirely as carnivores. This species, though, is an omnivore, occasionally eating seagrass.
Tiger Shark

Tiger Shark Facts
- Closing out this article about these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks comes the remarkable predator of the waves given the name of the Tiger Shark.
- This majestic product of Nature and evolution most frequently goes by the attention-grabbing common name we’ve given it here. Yet, the marvel of Nature has other general titles, as well. These include such terms as spotted shark and leopard shark, just to name a few.
- Within the community of scientific professionals, however, it’s possibly much better known by another one. That’s its technical moniker. Unfortunately, though, that’s a somewhat difficult one for the layperson to pronounce. It holds the official tag of Galeocerdo cuvier.
- The impressive animal received that tongue-twisting epithet after to the actions of the duo of François Auguste Péron and Charles Alexandre Lesueur. The two French naturalists achieved the first recognition of the creature as a separate and distinct species in the year 1822.
- Yet, that was not the name these researchers applied to it. They named the fish Squalus cuvier. Subsequently, later actions changed its designation several times. In 1837, another team assigned it the tag Galeocerdo tigrinus. But, it eventually received its current label.
- Unfortunately, the amazing Tiger Shark presently finds itself in dire straits. Its population base appears to be dwindling rapidly. Regrettably, that state seems to hold true across its entire range. The IUCN thus presently lists the animal as Near Threatened on its Red List.
- It’s currently facing serveral threats to its continued existence as a species. Like other species, most of these dangers stem from the actions of man. It faces the perils of commercial fishing practices, for one. It’s also now facing the dangers posed by habitat loss and climate change.

Tiger Shark Physical Description
The fascinating Tiger Shark fully merits the appreciation and respect it’s shown by those who encounter this amazing fish. Unlike some relatives, however, it does so not only because of its intriguing apperance. This creature also reaches highly respectable physical dimensions.
In that regard, though, it does maintain the pattern common among its many relatives. That’s due to the fact that the shark displays a certain degree of the physiological characteristic of sexual dimorphism. Yet, in its particular case this evolutionary trait manifests itself solely in terms of size.
More specifically, females of the species attain greater average measurements than their male counterparts. Mature females reach mean lengths of approximately 12.2 ft (3.7 m). Exceptional specimens exist, however. Confirmed examples sometimes grow up to 16.4 ft (5 m).
Weights of females also average greater than males, sometimes significantly so. Exceptional specimens of this sex occasionally exceed the extraordinary mass of as much as 2,900 lb (1,315 kg). Few individuals ever reach this great of a size, though, with most known specimens being smaller.
Males of the remarkable animal, meanwhile, remain somewhat smaller, sometimes much more so. For them, a typical body length measures around 10 ft (3 m). Rarely, an individual exceeds this size, but not greatly. Reliably confirmed reports puts the longest known male at 13.1 ft (4 m).
Since their lengths remain less, it’s only natural that the weight of this gender also measures less. For them, a mean body mass ranges from between 1,200 – 1,400 lb (544 – 635 kg). Naturally, a few exceptional examples do manage to grow beyond this size, but rarely by very much.
Otherwise, the genders of the impressive Tiger Shark present the same general appearance. Above, the overall color scheme generally consists of various shades of either light green or blue. Underneath, however, various shades of a pale yellow predominate, and rarely an off-white hue.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Galeocerdonidae
- Genus: Galeocerdo
- Species: G. cuvier
Tiger Shark Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The amazing Tiger Shark evolved as native to a comparatively broad expanse of the marine regions of the globe. The full extent of that zone habitation might surprise you, though. That’s because this wonder currently appears in nearly all of temperate and tropical waters around the world.
The exception to this pattern of habitation remains its lack of presence in the Mediterranean Sea. A few areas of the world do seem to show greater presences, however. Some of these include the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, and offshore of Australia, Indonesia, China, Africa, and India.
Yet, within that vast expanse of numereous seas and oceans, this true biological marvel displays a distinct preference regarding its choice of habitat. That’s true since the fish mainly, though, not exclusively appears relatively close to the coastline. It even approaches the shore after prey.
Even when it does appear somewhat near the shore, however, it generally prefers relatively deep waters. These regions also typically coincide with the presence of reef systems. Although the animal usually stays at relatively moderate levels, it’s been spotted at depths up to 3,000 ft (914 m).
The Tiger Shark feeds as one the apex predators of the oceans. It’s not a selective hunter, though, with a reputation for eating virtually anything. Though its diet principally consists of fish, it also consumes many crustaceans, sea snakes, seabirds, seals, and numerous others.
Given its significant size and power, this majestic denizen of the depths itself has very few natural predators. In fact, the only confirmed natural foe the animal faces in this respect is the Orca. Outside of such fates, it’s not known with any certainty how long the species lives.

7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks
We hope that each of you enjoyed reading, and hopefully learning something from, this article we’ve written for you about these 7 Stunning Atlantic Ocean Sharks. It’s also our fervent hope that doing so has left each of you with either a new or renewed appreciation for such wonders of Nature.
Unfortunately, however, many of their kindred located around the world now find themselves facing strong threats to their continued existence as a species. Many of those multiple dangers, in fact, stem from the actions of mankind. We must do all that we can to protect and preserve them all.
Check out our other articles on 4 Intriguing New Zealand Insects, Earth’s Amazingly Abundant Avians, 5 Remarkable West Virginia Invertebrates, The Mighty Tornado























Leave a Reply