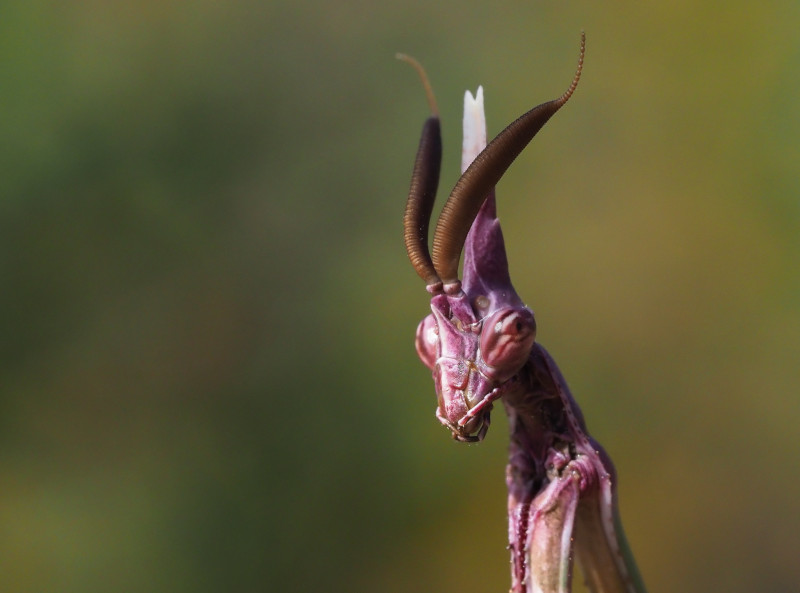

Conehead Mantis Facts
- The highly evocative term of the Conehead Mantis appropriately serves as the common name for this remarkable insect. This marvel of Nature and evolution also goes by another name, though. That’s its somewhat difficult to pronounce scientific name of Empusa pennata.
- Regardless of which of these terms one chooses to use for it, however, it remains blessed with a distinctive appearance. The preferred common name, quite understandably, derives from the presence of the incredible structure on the top of the awesome invertebrate’s head.
- The first recorded scientific recognition of this fantastic creature as a separate and distinct species occurred in the year 1815. That formal recognition took place as a result of the work of the well known Swedish naturalist, Carl Peter Thunberg, who also applied the epithet.
- For the moment, the marvelous Conehead Mantis appears to be maintaining a stable and sufficient population. This further seems to be the case throughout the entirety of its range. As a result, the IUCN list the species a Least Concern on its Red List of Threatened Species.
- The invertebrate must nevertheless be considered to be facing at least some threats to its continued existence as a species. One of these probably consists of the danger posed by increasing habitat loss. Its greatest threat, however, likely consists of ongoing climate change.
Related Articles

European Mantis
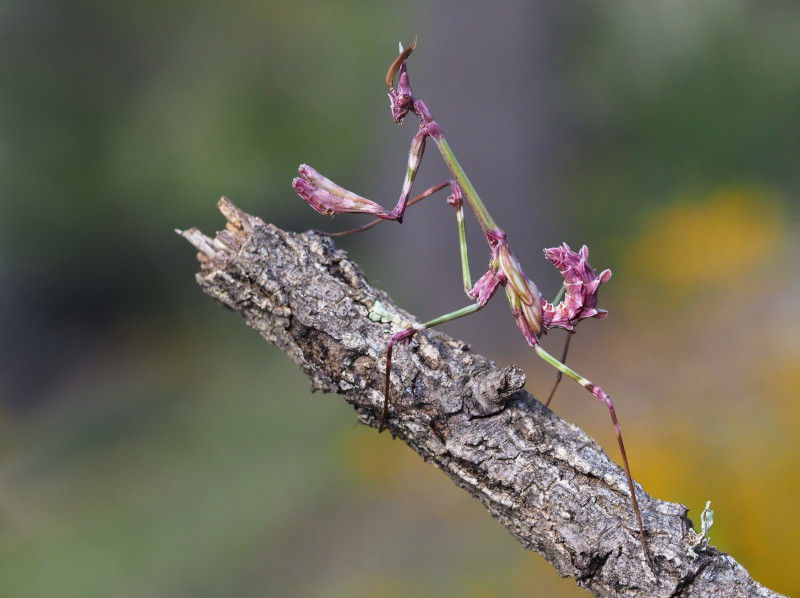



Conehead Mantis Physical Description
Although the marvelous Conehead Mantis fully deserves appreciation from those who view it, this does not derive solely from its sheer physical size. That aspect of the invertebrate does nonetheless rank as respectable, since the insect represents an above-averaged size variety of mantis.
Like most of its relatives across the globe, it also displays a moderate degree of sexual dimorphism. In its specific case, this trait manifests itself in two separate ways, though. Simple physical dimensions form the first of these, with the females attaining a slightly greater length than males.
This wonder of Nature and evolution achieves an average size slightly greater than the European Mantis. That being said, females reach an average length of about 4 in (10 cm). The smaller males, meanwhile, attain varying lengths, but rarely grow beyond 3 in (7.6 cm) in their total length.
The second form of gender-based differences among the remarkable Conehead Mantis appears in the form of the antennae of the male. These appendages generally possess a fine, feathery characteristic. However, only the male of the dazzling species develops these distinctive features.
Otherwise, the genders remain extremely similar in appearance. The colors vary, since it employs active camouflage, but certain ones are more common. These consist of green, pink, and various shades of brown. Its most noticeable feature, though, is the cone-shaped structure on the head.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Mantodea
- Family: Empusidae
- Genus: Empusa
- Species: E. pennata
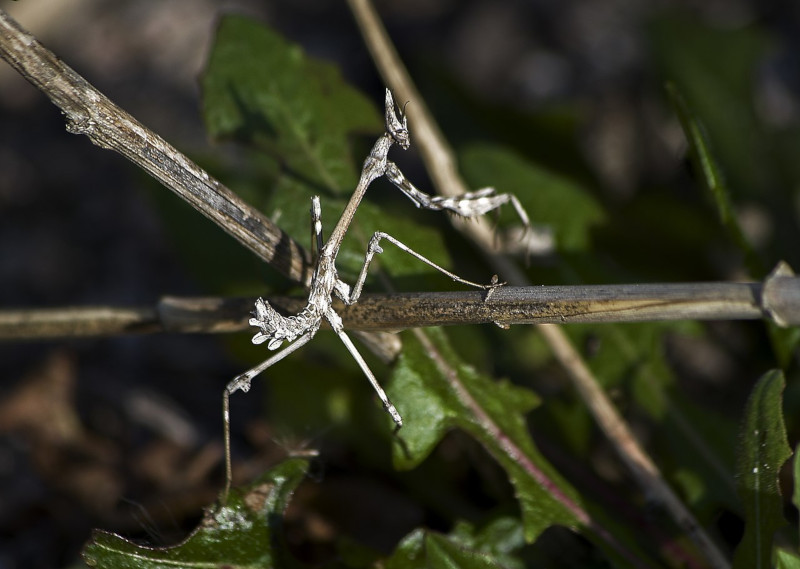

Conehead Mantis Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The remarkable Conehead Mantis possesses a comparatively broad, if somewhat broken, range of habitation across the world. It’s broad because it covers parts of both Europe and Asia. It’s also broken, though, since it only appears in scattered parts of the two continents, not evenly.
More precisely, in Europe, the astonishing Arthropod seems to live within the countries of France, Portugal, Spain, Italy, Bulgaria, and Greece. In Asia, meanwhile, its only known habitat consists of the country of Lebanon. The exact for this pattern presently still remains undetermined.
In all of the regions of the globe in which it appears, however, its habitat preference remains decidedly the same. This specific form of mantis demonstrably prefers to inhabit more open areas, as opposed to denser forest regions. This mainly includes regions of scrub and perennial herbs.
The amazing Conehead Mantis prefers to reside within such regions because of its feeding habits. Like its many relatives, it evolved purely as a carnivore. It also feeds as an ambush predator. This powerful and efficient hunter eats a vast variety of small insects native to the same habitat.
In turn, the powerful hunter eventually falls prey to other, even larger predators. These threats usually vary according to its particular area, of course. Overall, however, these mainly include such animals as snakes, frogs, lizards, and a wide variety of avian species sharing its own region.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on 5 Deceptively Dangerous Herbaceous Plants, Indian Bullfrog, Seven Rila Lakes, Woylie, Quiver Tree, Satanic Leaf-Tailed Gecko, Leona’s Little Blue, Tiger Shark









Leave a Reply