Lake Kaindy Facts
- This breathtaking, otherworldly geological formation most frequently goes by the remarkably simple title of Lake Kaindy. Yet, it does have a few other monikers by which its also known. These include the terms Sunk Forest Lake, and the simple reversal of the other, Kandy Lake.
- Though the location of the lake can’t be called particularly remote, the surrounding terrain has a daunting nature. That’s due to the fact that the terrain of the region can be quite rugged. As a result of this, the scenic beauty of the formation still receives relatively few visitors.
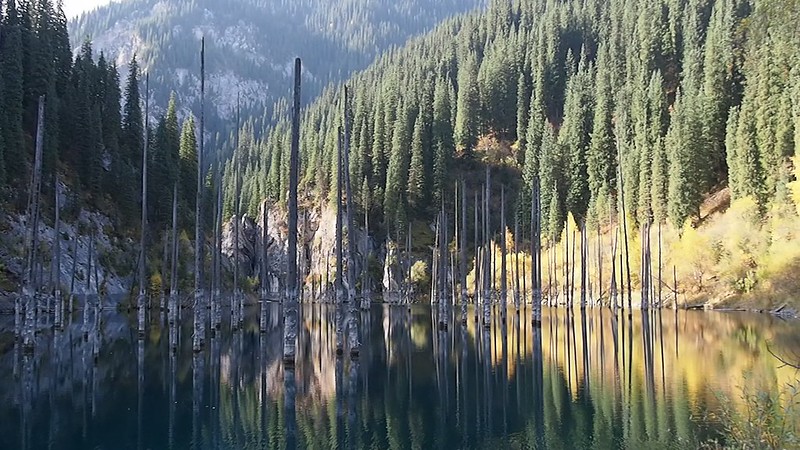
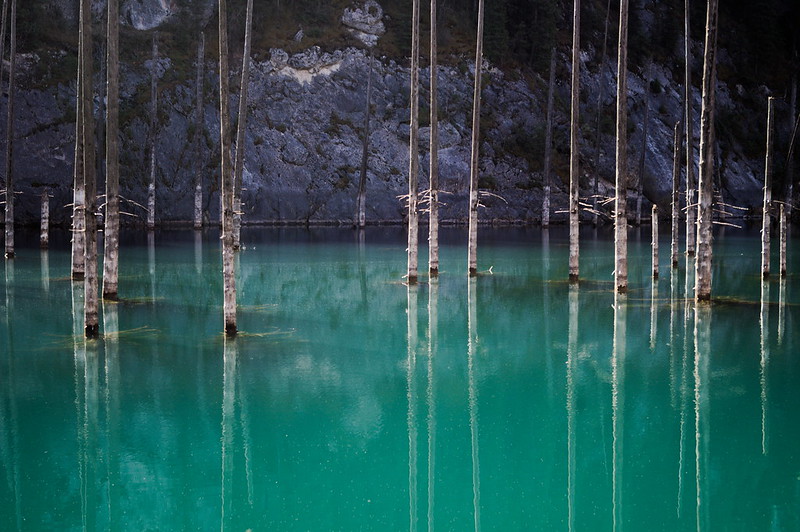
- Perhaps the most noteworthy aspect of the remote lake actually involves what lies within the lake itself. That’s because its pristine waters contain a surprise for those who visit it. It holds a small forest, which has been completely upturned and preserved relatively unchanged.
- The extraordinary geological marvel known as Lake Kaindy has a remarkably recent time of origin. That’s because this marvel also has a highly unexpected twist to it. Astoundingly, the wondrous site actually formed relatively recently due to a powerful geological event.
- Fortunately, this recently formed miracle of Nature now enjoys a certain measure of protection from the depredations of man. The mesemrizing body of water presently forms a central part of the Kolsai Lakes National Park. Environmental regulations exist to protect its ecosystem.
Related Articles



Lake Kaindy Physical Description
The beautiful Lake Kaindy instantly entrances virtually everyone who encounters the masterpiece, especially the first time. While it principally does so due to its sheer beauty, other factors nevertheless merit mention. That’s true since it also boasts some respectable measurements.
Though its dimensions vary somewhat, due to the same factors that affect most lakes, certain averages remain. In general, the feature measures approximately 1,312 ft (400 m) in length. Intriguingly, it also maintains a comparatively shallow mean depth equaling roughly 98 ft (30 m).
Not to be outdone, the water comprising the lake itself also possesses impressive attributes that distinguish it from many others around the world. For one, this remains extremely cold, often close to freezing. This remains true throughout the year, even during the summer months.
Its water further appeals to the visitor due to the dazzling color it presents one with. Most frequently this manifests as a startling shade of turquoise. That occurs because of a combination of glacial melt and limestone deposits. Minor variations of this color do occasionally occur, though.
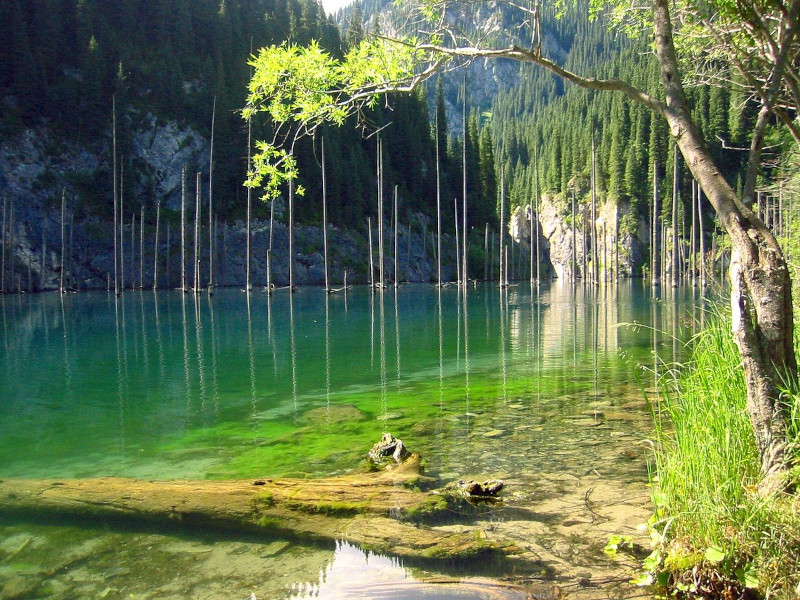
Yet without doubt, the most unforgettable feature of Lake Kaindy continues to be what lies within its confines. Protruding from within its depths, numerous tree trunks extend upward various distances! Turned upside down, while these reach upward, their crowns lie beneath the surface.
Comprised almost entirely of the remains of a locally numerous species of spruce tree, their presence creates an unearthly ambiance around the location. The extreme natural frigidity of the water itself further adds to this by maintaining their virtually pristine state since the lake’s creation.

Lake Kaindy Location, Formation, and Distinctiveness
The mind-blowing uniqueness of Lake Kaindy formed in a region of the globe already well known for its abundance of natural wonders. In its case, however, it formed in a somewhat remote portion of that area. That’s due to the fact that it lies within the central section of the continent of Asia.
There, this marvel of geology resides within the national borders of the country of Kazakhstan. Nature created this remarkable formation, albeit as a byproduct of a natural event, in the Tian Shan Mountains. Its precise placement puts it roughly 81 mi (130 km) east of the city of Almaty.
Yet another result of its fairly recent creation derives from that setting. Because it appeared inside the area of this mountain range, it also lies at a much higher altitude than most lakes. Indeed, the surface of the water sits at an average altitude of about 6,600 ft (2,000 m) above sea level.
As alluded to previously, this gorgeous tarn formed in what amounts to virtually yesterday in geological terms. Its amazing formation took place in the year 1911. At that time, a powerful 7.7 earthquake shook the surrounding mountains in which the lake now finds itself nestled.
The earthquake triggered a massive landslide, comprised principally of the locally abundant limestone. This vast amount of debris subsequently blocked the Kaindy River, creating a natural dam. Over time, the valley behind this natural dam slowly filled with water, forming the lake.
Its most eye-catching feature, the uprooted and vertically placed trees, also arrived via the same action and at the same time. The landslide brought these down the slopes of the gorge in which the landslide occurred. They plummeted to their current resting place, where they remain today.
Lake Kaindy has a unique ecological system strongly influenced by its high altitude and the nature of its waters. The latter affects this in two ways. The nature of its surrounding ecosystem owes a great deal to the combination of relatively high altitude and its specific mineral content.
The area immediately surrounding the lake supports a primarily alpine environment. Here, one finds a multitude of fir, spruce, and birch forests, along with meadows and wildflowers. Though relatively low in fish due to its cold temperature, small aquatic organisms and algae nevertheless exist.
Features Sharing Its Region


Check out our other articles on 10 Dazzling Denizens of the Depths, Rose of Jericho, Lowland Streaked Tenrec, American Burying Beetle, Seychelles Sheat-Tailed Bat, Tenerife, Serval, Fall Phlox











Leave a Reply