Black-Margin Cyerce Facts
- This eye-catching denizen of the depths most typically goes by the highly descriptive common name of the Black-Margin Cyerce. It does have a few other, if unusual, general titles it’s known by. These include the tags Black-Margined Sap-Sucking Slug and Sap-Sucking Slug.
- Within scientific circles, however, it’s perhaps significantly better known by its technical designation. Fortunately, that particular one’s much easier than most such for the layperson to pronounce. That’s because the intriguing creature holds the formal epithet Cyerce nigricans.
- The remarkable animal received that moniker due to the efforts of William Harper Pease. The widely respected American malacologist accomplished the first recognition of the creature as a separate and distinct species. He achieved that scientifically noteworthy feat in 1866.
- These sea slugs actually represent a vital resource for both marine biologists and ecologists alike. Its presence provides indications of the relative health of the local marine ecosystem. This holds particularly true of the specific communities the wonder of evolution inhabits.
- Thankfully, the amazing Black-Margin Cyerce seems to be continuing to hold onto a stable and sufficient population base. That situation also appears to hold true across its entire range. The IUCN thus currently has no listing for the mollusc on its Red List of Threatened Species.
- This marvel of Nature and evolution nevertheless still faces multiple potential threats to its continued existence as a species. Like all forms of life on earth today, most of these perils stem from the actions of man. They include the related dangers of habitat loss and climate change.
Related Articles



Black-Margin Cyerce Physical Description
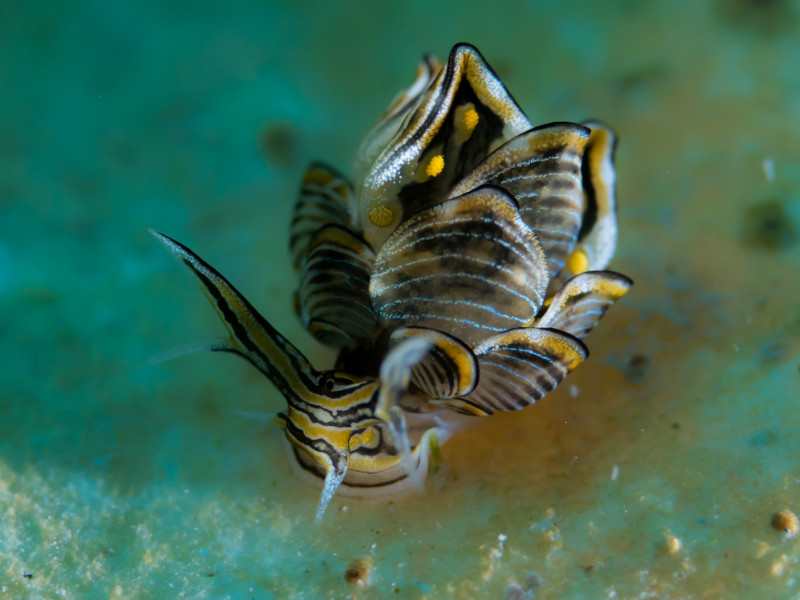
The astounding Black-Margin Cyerce clearly represents a creature designed by evolution to catch the eye of those individuals lucky enough to venture into its habitat. It understandably does so, however, due to its appearance, rather than its size. That’s due to the fact that it’s a small being.
It also distinguishes itself in this particular regard from the majority of animals in the world. Most of those display some degree of the physical trait of sexual dimorphism. Like its many relatives, though, this specific marvel instead evolved as a hermaphrodite, thus being both male and female.
All individuals therefore present approximately the same general outward appearance. In terms of total length, though, an average actually measures less than 0.8 in (2 cm). Though some exceptional specimens naturally occasionally occur, even these do not exceed this by any great amount.
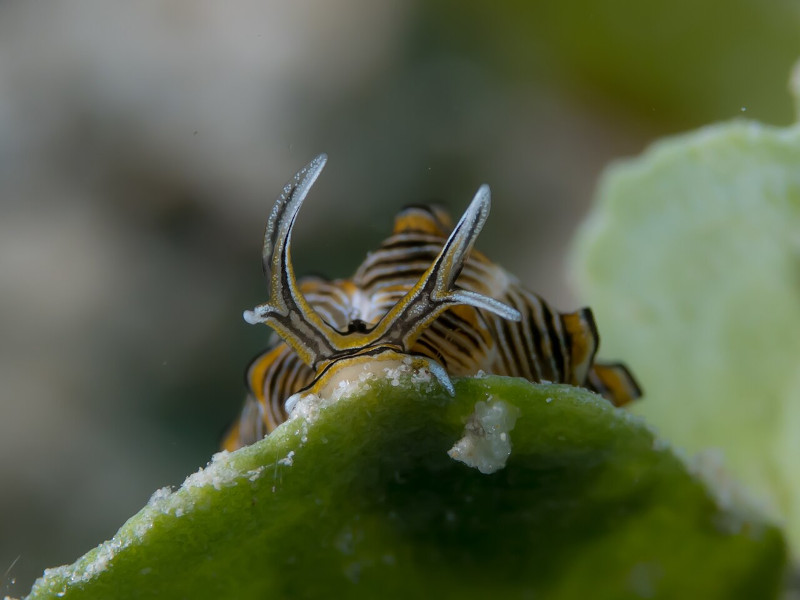
The body of this marvel also develops as notably elongated and flattened, following a pattern common among its numerous kindred. Like those same kin, its eyes remain small and located near the base of the rhinophores. They’re not highly developed, but do detect changes in light and dark.
Those same rhinophorse appear on the top of the head of mollusc. These features also often smooth and possess a slight tapering design. The foot, meanwhile, develops as primarily flat, broad, and muscular underside of the slug. It usually presents the same color as the rest of the body.
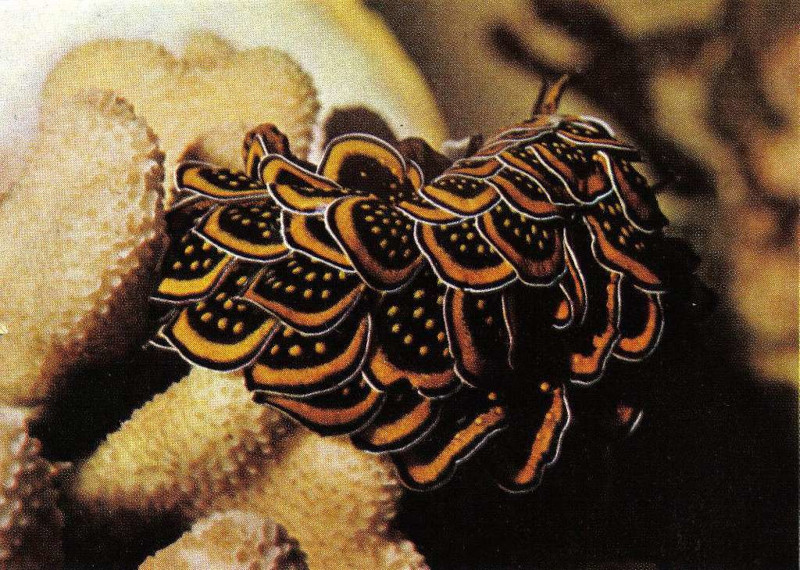
The body of the Black-Margin Cyerce appears translucent and exhibits multiple hues of green, blue, or orange. The coloration also varies depending on the individual and its diet. The most truly distinctive feature remains the black margins seen on its cerata, contrasting sharply with the rest.
Yet, it’s no doubt those cerata themselves that garner the most interest from the observer. These leaf-like appendages cover the back of the sea slug. They’re further arranged in rows, and sometimes quite numerous. Though mainly translucent, they’re also edged with a clear black margin.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Class: Gastropoda
- Order: Sacoglossa
- Family: Caliphyllidae
- Genus: Cyerce
- Species: C. nigricans
Black-Margin Cyerce Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The marvelous product of Nature and evolution named the Black-Margin Cyerce evolved as indigenous to a moderately broad portion of the marine regions of the globe. Just exactly where that natural zone of habitation lies nonetheless might surprise a few of our loyal readers, however.
It evolved as native to several portions of the tropical and subtropical regions of the Indo-Pacific. This broad area encompasses a fairly large part of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, including the waters around Southeast Asia, Australia, and the islands of the Central and Western Pacific.
Its presence remains highly scattered, however. In Southeast Asia, it’s mostly seen just off the coasts of Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Thailand. In Australia, it mainly lives along the northern shores. Island locations include such places as Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands.
The remarkable sea slug additionally displays an impressive adaptability regarding its choice of habitat within its range. It therefore inhabits a wide range of marine environments set inside its area of distribution. All these do locations, though, naturally share certain basic requirements.
The sea slug’s often found residing within comparatively shallow waters where sunlight routinely penetrates, promoting the growth of its primary food source. Seagrass meadows also provide an ideal habitat for the animal due to the abundance of algae growing on the seagrass blades.
Intertidal zones and coral reefs also form a common location for its presence to be seen. The nooks and crannies of the reef offer protection from predators and strong currents. Rocky areas with ample algal growth are also common habitats. The hard surfaces allow algae to attach and thrive.
The captivating Black-Margin Cyerce also evolved a highly specialized diet. It primarily feeds on types of algae. As a sap-sucking slug, it utilizes a very specialized feeding organ called a radula to scrape and consume algal cells. This feeding strategy helps control algal populations in its habitat.
This very intriguing creature also evolved as hermaphroditic in its nature, meaning that each individual possesses both male and female reproductive organs. This trait allows any two individuals to mate and exchange sperm, further increasing the species’ reproductive opportunities.
Following mating activities, however, the highly colorful creation of evolution lays its numerous eggs in gelatinous masses attached to the substrate. It also often does so in large numbers. The eggs later develop into larvae, which eventually settle and metamorphose into juvenile sea slugs.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on 4 Remarkable Reptiles of Thailand, North Atlantic Right Whale, Mammoth Hot Springs, Pale Umbrella Orchid, Purple Frog, Tree Bumblebee, Jewelled Gecko












Leave a Reply