
Kauri Tree Facts
- This impressive work of Nature most frequently goes by the deceptively short common name of the Kauri Tree in most parts of its range. It does have a few other general titles it’s known by, though. These include the terms Dammar pine and Kauri pine, among several others.
- Still other tags include the informative one of New Zealand Kauri. It’s used to distinguish the flora from other members of its genus in other areas. In the language of the local Indigenous People, however, this true marvel of evolution holds the original designation Kauri.
- Within the scientific community, though, it’s perhaps much better known by still another, separate appellation. Thankfully, that’s a relatively easy one for the layperson to pronounce. That’s due to the fact that the amazing plant currently holds the moniker Agathis australis.
- The marvel of Nature received that designation due to the efforts of Richard Anthony Salisbury. The highly respected British botanist accomplished the first official recognition of it as a separate and distinct species. He achieved that scientifically noteworthy feat in the year 1807.
- The situation of the remarkable Kauri Tree is somewhat unusual. Its population remains reduced and scattered, to be certain. Only small, concentrated pockets of the wonder remain. Despite this state, however, the IUCN does not list it on its Red List of Threatened Species.
- The stunning wonder of evolution obviously faces multiple threats to its continued existence as a species. These dangers include local problems, such as deforestation. Yet, the tree also faces the global perils faced by all life today, those of habitat loss and ongoing climate change.
Related Articles



Kauri Tree Physical Description
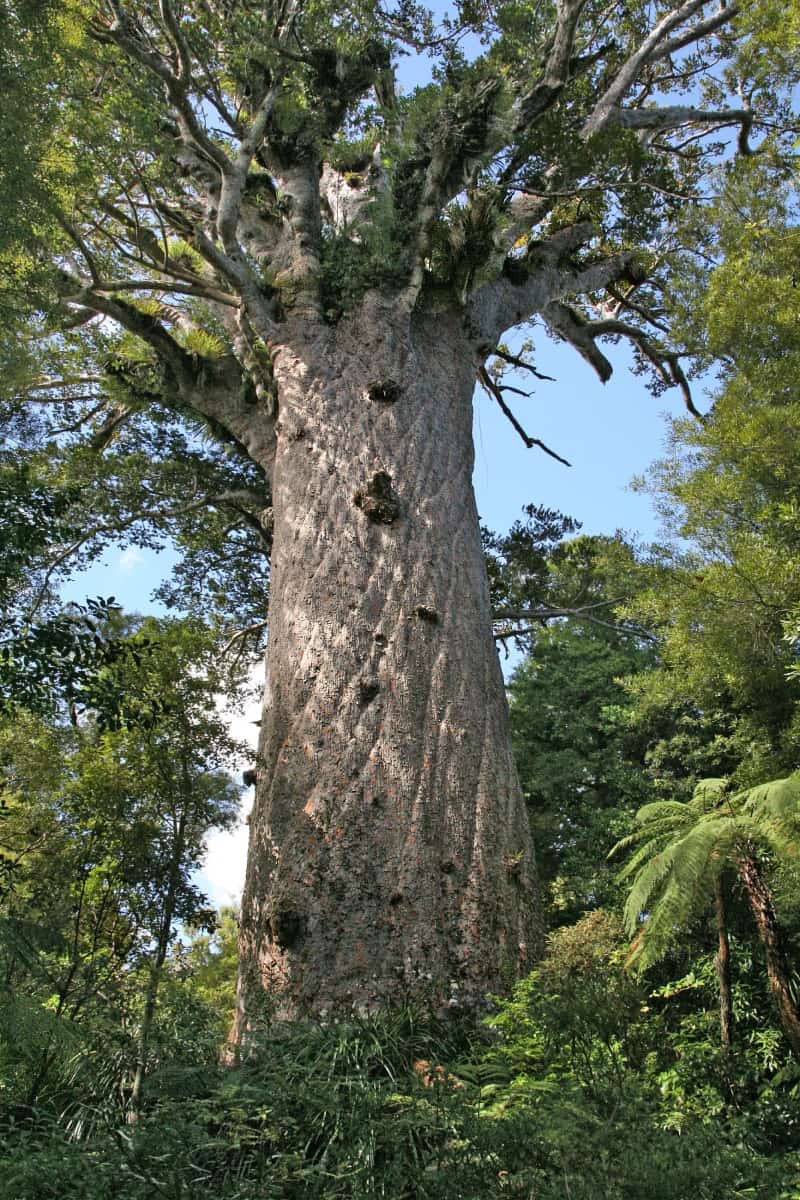
The fabulous Kauri Tree almost always impresses those individuals fortunate enough to view it. Unlike some flora, though, this marvel does so for a variety of reasons. That’s true since this plant’s not only distinctive and beautiful in appearance, but also attains eminently respectable sizes.
Fully mature specimens typically reach truly eye-catching proportions. These examples occasionally reach heights measuring as much as an astounding 164 ft (50 m). The great majority of these impressive Tracheophytes, however, typically range from approximately 98.4 – 131.2 ft (30 – 40 m).
The trunk of the tree itself generally grows primarily quite vertically, with comparatively little deviation. It’s also quite cylindrical in shape and width. This part typically ranges from 6.6 – 16.4 ft (2 – 5 m)! Some truly exceptional specimens of the mesmeric species have even larger girths.
Even the covering of this staggering trunk stands out from many of its relatives around the globe. This feature evolved as thick and corky in structure. It also has a surprising tendency to flake off in large, thick strips. This unique texture helps to protect the tree from damage and disease.
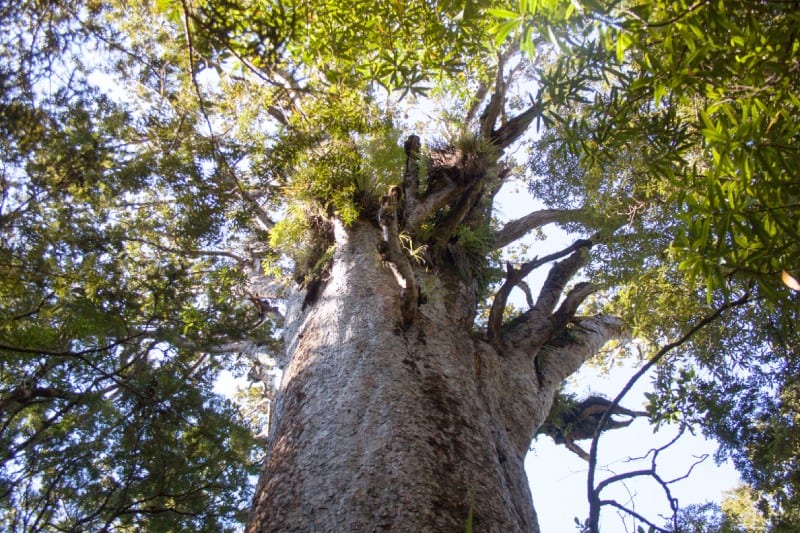
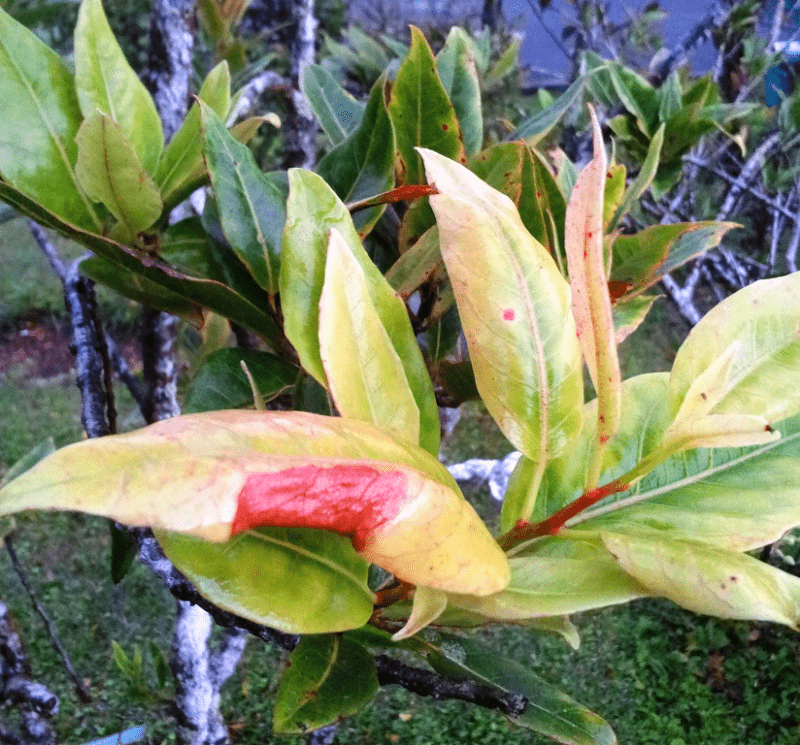
Its leaves also serve to augment its intriguing appearance and visual appeal. This foliage develops as oblong in shape, with a leathery texture. Arranged in pairs along the branches, these range in length from 0.8 – 2.8 in (2 – 7 cm). Colored dark green, they’re glossy above and pale beneath.
The branches of crown of the Kauri Tree additionally serve to set it apart. This typically forms as dense and quite rounded. In mature trees, the lower one’s may fall off, resulting in a tall, bare trunk with a high canopy. These spread horizontally, becoming massive, creating a wide canopy.
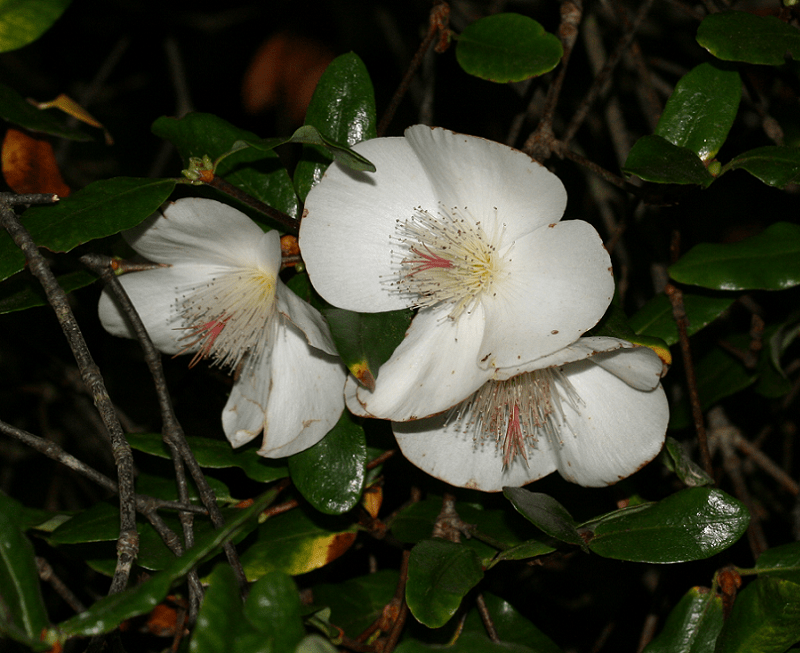
This wonder of Nature and botanical evolution also evolved as coniferous. It therefore possesses sed cones. In its case, it has both male and female cones. The male cones remain somewhat smaller and more rounded than the females. Holding seeds, female cones measure up to 2.8 in (7 cm).
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Phylum: Pinophyta
- Class: Pinopsida
- Family: Araucariaceae
- Genus: Agathis
- Species: A. australis
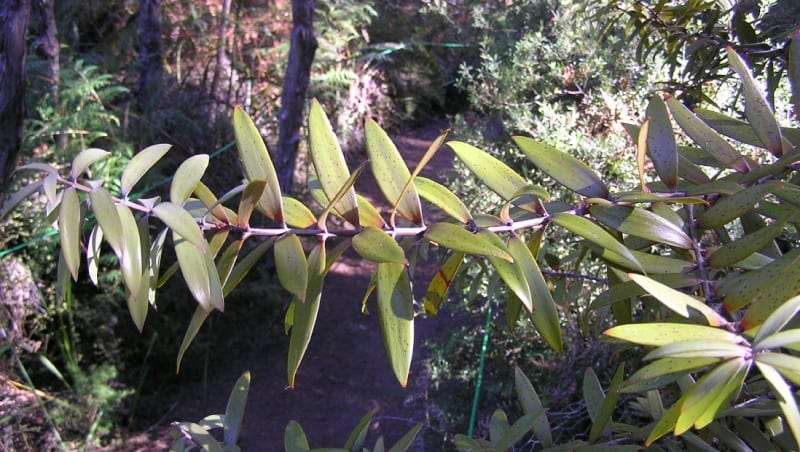

Kauri Tree Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
Sadly, the stunning Kauri Tree evolved as native to an extremely limited portion of the surface of the earth. The exact location of where that zone of habitation lies won’t surprise many people, though. It’s native to the stunning country of New Zealand, located near the continent of Australia.
Yet, even in this isolated part of the world, this remarkable flora only appears in a small portion of this already restricted habitat range. That’s because it only lives on North Island. Further reducing its territorial range comes the fact that it also only inhabits the northern regions of this site.
The Northland Peninsula serves as the heart of this range, and holds the majority of specimens. South of this, though, the species also appears within the Aukland Region, though only in fragmented populations. The Waikato Region represents the southernmost part of its territory.
It also displays decidedly specific requirements for its habitat preferences, further reducing its chances for expansion. The tree typically grows in mixed forests, alongside various other native species such as rimu, totara, and taraire. These forests are characterized by their rich biodiversity.
It also prefers well-drained, acidic soils and specimens are commonly found growing on ridges and slopes where water does not accumulate. However, it also grows in a variety of soil types, including sandy, clayey, and rocky substrates. It lives from sea level up to about 2,000 ft (600 m).
Given its precise nature, the Kauri Tree achieves its pollination via the actions of the wind. Male cones release pollen into the air, especially during dry and very windy conditions, which facilitate dispersal. This then gets carried away by the wind and some of it lands on the female cones.
It also plays a vital role within its insulated ecosystem. The canopies of these marvels provide a unique habitat for an impressive variety of plant species, including plants that grow on other plants, known to science as epiphytes, and understory plants adapted to lower light conditions.
Its presence also supports a surprisingly wide range of indigenous animal species. Numerous birds, insects, and other wildlife find food, shelter, and breeding sites within these forests. The dense canopy and thick bark additionally offer protection and nesting sites for a number of local species.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on Rainbow Eucalyptus, Buddha’s Hand, Macquarie Island, Yellow Throated Marten, Giant Wood Moth, Wilson’s Bird-of-paradise, Sea Lamprey, Hermann’s Tortoise









Leave a Reply