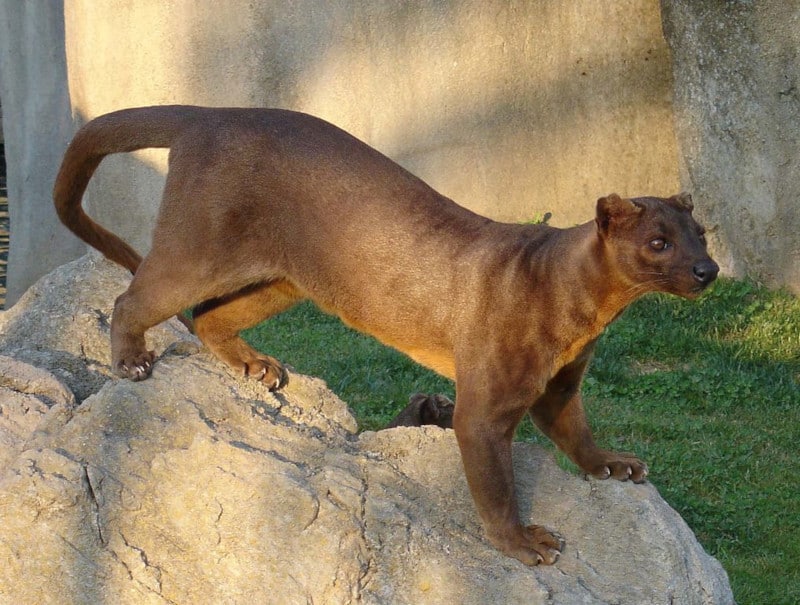

Fossa Facts
- This highly fascinating mammal most frequently goes by the short, and somewhat confusing common name of the Fossa. That’s true due to the unusual fact that this same term also represents the generic name of another species in the local area.
- Within scientific circles, however, it’s often known by its technical monniker. Like so many such terms, though, it’s fairly difficult for the layperson to pronounce. That’s because this distinctive creature holds the official title of Cryptoprocta ferox.
- The intriguing animal received that appellation due to the efforts of Edward Turner Bennett. The The British zoologist accomplished the first formal recognition of it as a separate and distinct species. That scientifically notable deed occurred in the year 1833.
- Presently, the population of the Fossa appears to be comparatively stable. Unfortunately, the density of those numbers seems to quite low. Given this situation, the IUCN currently lists the animal as Vulnerable on the organization’s Red List.
- It faces multiple potential threats to its continued existence as a species. Like most, many of these stem from the actions of man. Its most immediate peril consists of habitat loss. It also now faces the looming threat posed by climate change, as well.
Related Articles




Fossa Physical Description
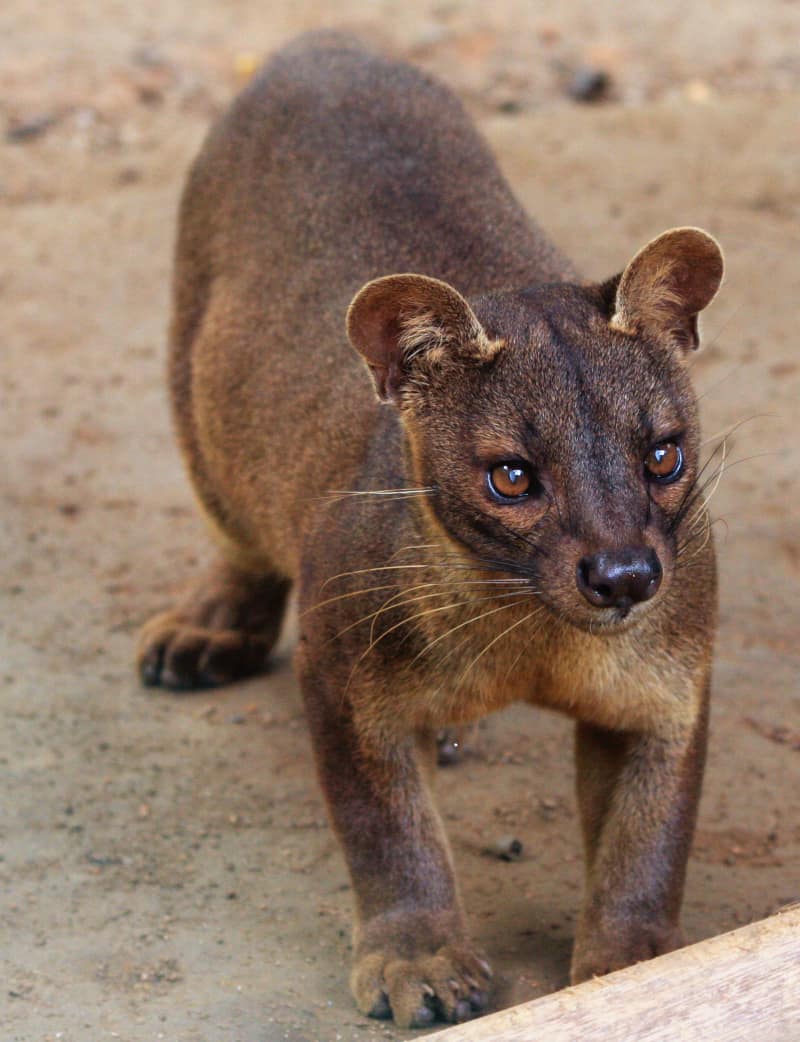
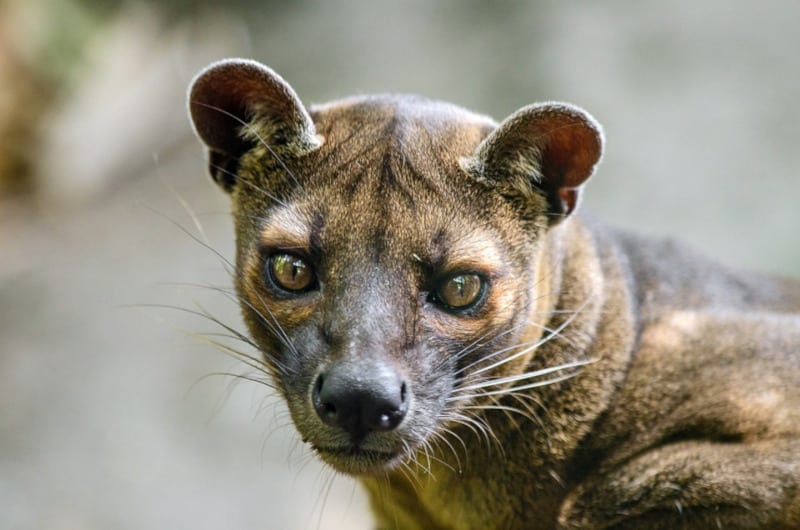
The fabulous Fossa represents a truly distinctive creation of Nature and evolutionary processes. Despite its definite feline-like appearance, though, it holds no relationship with cats. It developed similar traits independently, via a process known as convergent evolution.
Like many creatures, including felines, it displays a certain degree of the physiological characteristic known as sexual dimorphism. In its case, this trait manifests itself purely in terms of physical size. However, the gender-based difference generally remains slight.
Due to this attribute, males typically grow larger than females. These attain an average head-body length measuring between 28-31 in (70-80 cm). The tail grows quite long in relation to the body. This appendage reaches a mean length of 26-28 in (65-70 cm).
Females achieve approximately the same measurements as males, in this specific regard. The distinction occurs in terms of mass. Males usually average 14-19 lb (6.2-8.6 kg). Yet the females only average 12-15 lb (5.5-6.8 kg). These thus tend to present a slimmer shape.
Otherwise, the sexes of the Fossa present the same appearance. The fur develops as short and straight in nature. It also grows dense, and typically without noticeable patterns or spots. The upper part shows a reddish-brown, while the underside shows a cream hue.
The amazing animal also boasts several fascinating physical attributes that set it apart from many others. It has semi-retractable claws on its feet. Incredibly, those same feet possess flexible ankles. The head’s elongated, and displays comparatively wide-set eyes.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Eupleridae
- Genus: Cryptoprocta
- Species: C. ferox

Fossa Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The extraordinary Fossa evolved as native to an equally incredible portion of the globe. Unfortunately, however, that’s zone of habitation is also very limited. When learning of that region, though, very few people find that habitat range surprising at all.
That’s because this awesome marvel of Nature only lives on what’s now known as the equally unique island of Madagascar. Even there, however, the impressive animal appears in scattered low-level concentrations in only certain parts of the greater overall range.
Like many related species in the wild, it displays decided preferences regarging its choice of habitat. The largest percentage of its remaining numers make their home in sections of undisturbed, relatively pristine forest areas. Small numbers do live in degraded forests.
While the mammal resides in all types of forests on the island, it presents preferences in that manner, as well. Most individuals inhabit areas of dry deciduous forests, spiny forests, and rainforest. It definitely prefers more humid types of these than drier habitats.
The Fossa evolved to be equally active by both day and night. It’s also typically solitary in behavior, except for females raising their young. Individuals rarely display any form of aggressive behavior, except for males during breeding season, while competing for females.
It evolved as carnivorous in terms of its diet. The animal also represents one of the top predators on the island. Prey typically consists of small-to-medium sized animals, especially lemurs. Except for falling victim to the occasional crocodile, it has no natural predators.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on 4 Gorgeous European Gorges, Quokka, Great Barrier Reef, Long Eared Jerboa, Orange Jewelweed, Sambar, Borneo Bay Cat, Caracal, American Alligator









Leave a Reply