
Jeita Grotto Facts
- This marvel of Nature, largely unknown outside of its immediate area, goes by the name of the Jeita Grotto. Perhaps most notably, however, the breathtaking site isn’t just another cave. That’s because it is significantly important to the region it formed in.
- That importance isn’t restricted to just one way, though. In point of fact, it’s impact on the region occurs in cultural, social, and even economic ways. The fabulous site has, in fact, played a relatively major role in the region since long before our modern era.
- Archaeological evidence indicates that ancient man used the lower section in prehistoric times, and over an extensive period. Researchers have yet to find any sign of use during that same period in the upper section, though inverstigations continue.
- For reasons yet to be determined, its ancient inhabitants apparently abandoned it long before modern times. Reverend William Thomson accidentally rediscovered it in 1836, while exploring. It appears to have been completely unknown during the interim.
- Due to its importance to the region, it now serves as the national symbol of the country it lies in. It’s magnificence does not go unnoticed now, though. The Jeita Grotto made the final round of consideration in the New 7 Wonders of Nature competition.
Related Articles
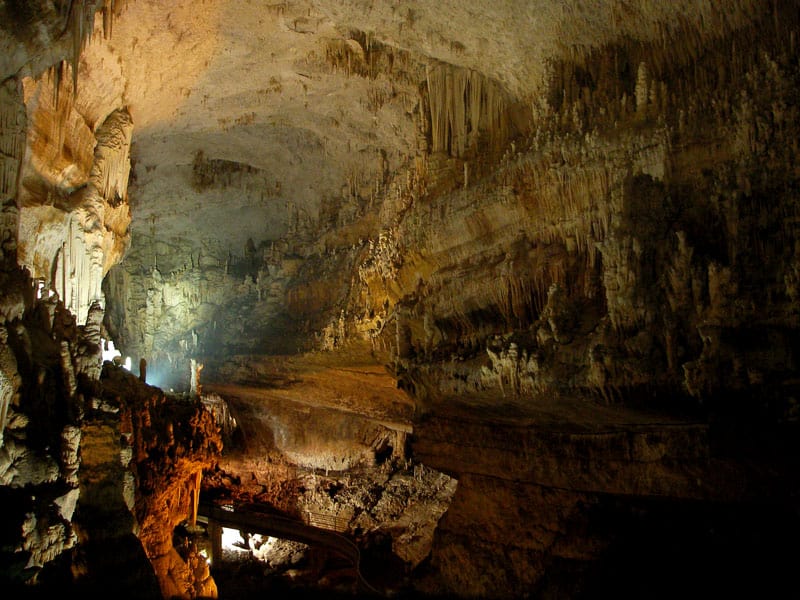




Jeita Grotto Physical Description
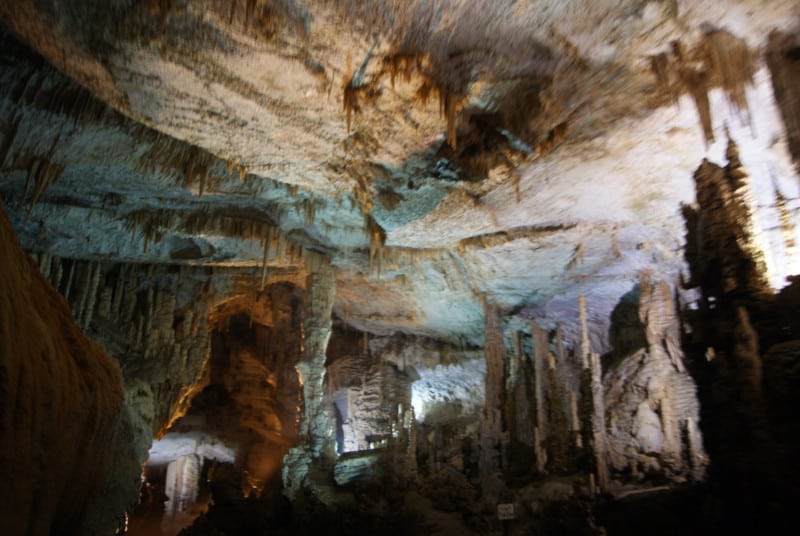
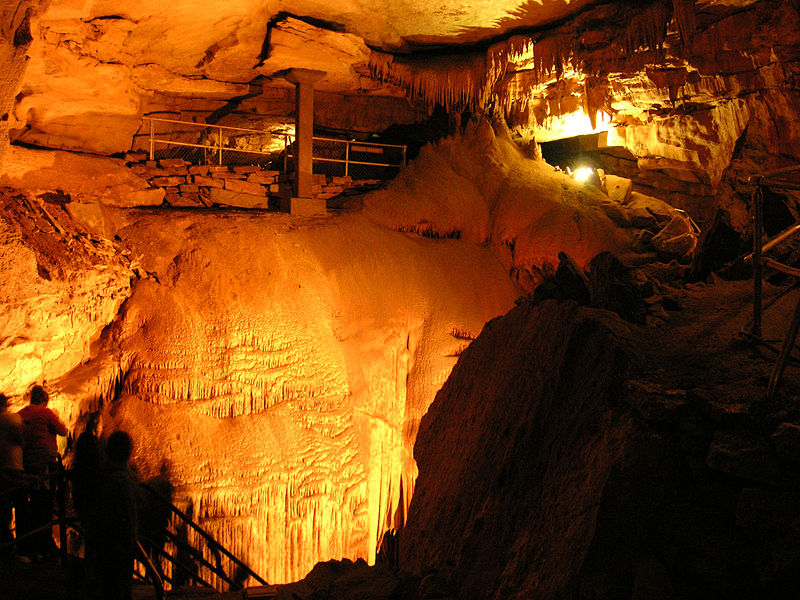
The stunning Jeita Grotto holds many surprises for its visitors. This begins with the fact that it’s actually a system of two caves. While these remain separate, the caves interconnect. Together, the amazing system possesses an overall length totaling about 5.6 mi (9 km).
Because of its size, it ranks as the longest cave system in its part of the world. The upper cave measures roughly 6,990 ft (2,130 m) in length. The lower section, meanwhile, measures about 20,300 ft (6,200 m) long. Heights also vary, but reach as high as 39 ft (12 m).
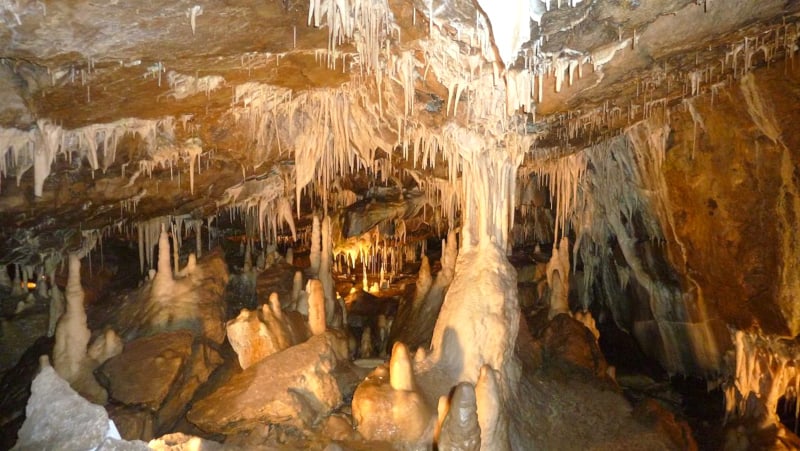
It musn’t be overlooked, though, that this marvelous location houses many individual wonders, as well. These include columns, ponds, curtains, stalactites and stalagmites. In fact, it also holds the largest known stalactite in the world, at 27 ft (8.2 m) long.
It also contains three huge, separate natural chambers, as well as a subterranean river. The largest of the chambers measures an impressive 390 ft (120 m) long. The river it holds further serves as the source of drinking water for 1.5 million local residents.

Jeita Grotto Location, Geology, and Importance
The dazzling site now called the Jeita Grotto formed in an area of the world already renowned for its many remarkable natural features. That’s because the dazzling dual cave system formed in what mankind now knows as the country of Lebanon, in western Asia.
Within that region, the cave system sits about 11 mi (18 km) from the city of Beirut. That location makes its remaining unnotieced so long even more amazing. Its location places it on the western side of the Lebanon Mountains. More precisely, it’s in the Nahr al-Kalb valley.
Adding to its splendor is its proximity to the coast. Incredibly, the system sits only 3.1 mi (5 km) from coast of the Mediterranean Sea. This location places it in the Nahr al-Kalb valley. Its naturally formed opening lies approximately 330 ft (100 m) above sea level.
Not only the area around the Jeita Grotto, but the entire region has a largely limestone geology. This therefore allowed for the formation of the impressive limestone karst caves. The process further occurred over a currently undetermined span of millennia.
It now has rather varied usefulness in the region. Most notably, it remains one of the most important tourist sites in the region. But sadly, its use as a water source may soon come to an end. Pollution levels in the water due to agricultural runoff has begun to increase.
Features Sharing Its Region


Check out our other articles on 5 Island-Evolved Herbaceous Plants , Thresher Shark, Tree Kangaroo, Clouded Sulphur Butterfly, Black Rain Frog, Hyacinth Macaw, Olive Ridley Sea Turtle









Leave a Reply