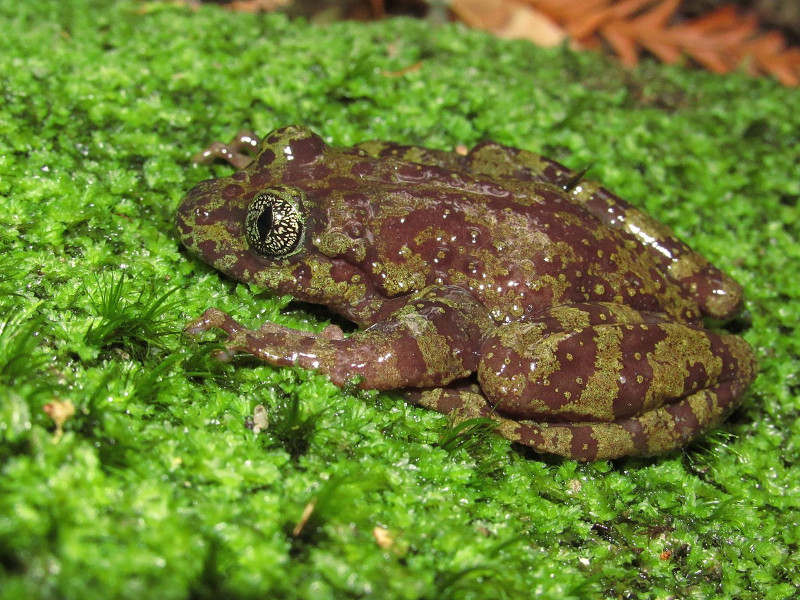

Rose’s Ghost Frog Facts
- The attention-grabbing term of Rose’s Ghost Frog serves as the most frequently used common name for this amazing Amphibian. It does have at least one other general title, though. That’s the closely related appellation of Table Mountain Ghost Frog.
- Within the scientific community, however, it’s perhaps better known by its technical designation. Fortunately for the layperson, that’s a comparatively simple label, as such things go. That’s because the frog holds the official moniker of Heleophryne rosei.
- The remarkable animal received that epithet due to the efforts of John Hewitt. The South African zoologist accomplished the first recorded recognition of the creature as a separate and distinct species. He managed that scientifically noteworthy deed in 1925.
- Unfortunately, the impressive Rose’s Ghost Frog possesses a highly limited range. It also appears to have an extremely small population. Due to these conditions, combined with other factors, the IUCN presently lists the small wonder as Critically Endangered.
- The most immediate threat to its continued existence that it faces comes from habitat change and outright loss. These mainly occur due to human activities. Yet, it also now faces the same growing danger of climate change that all of earth’s species currently do.
Related Articles




Rose’s Ghost Frog Physical Description
The incredible Rose’s Ghost Frog immediately captivates those fortunate enough to encounter one in the wild. Like most of its numerous relatives, however, it does not do so due to its sheer phsycial size. That’s true since this particular frog qualifies as average-sized.
In this regard, the animal follows a pattern common to many animals, including amphibians. That’s in the fact that it displays a certain degree of the physiological characterstic of sexual dimorphism. In its case, this trait manifests itself with females being larger than males.
The female attains an average body length measuring approximately 2.4 in (6.1 cm). Among the males, though, a mean length only equals about 2 in (5.1 cm). Exceptional individuals do occur, of course. These specimens, however, develop wholly regardless of their gender.
In terms of coloring, both sexes of this marvel of Nature present the same basic pattern. This principally consists of a pale green background. Nature augments this, however. Individuals develop varying patterns of blotches that range in color from a light brown to purple.
The awesome Rose’s Ghost Frog catches the eye of the observer in ways other than it’s simple physical dimensions, though. The fingers and toes of the Amphibian present large discs at their end. Intriguingly, these evolved to display a generally triangular shape.
Distinctively, the small feet themselves develop as only half-webbed in structure. It has five toes, with part of the fifth one being free of the webbing. In an extraordinary act of evolution, the creature also manifests a rudimentary thumb on the equivalent of its index finger!
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Amphibia
- Order: Anura
- Family: Heleophrynidae
- Genus: Heleophryne
- Species: H. rosei
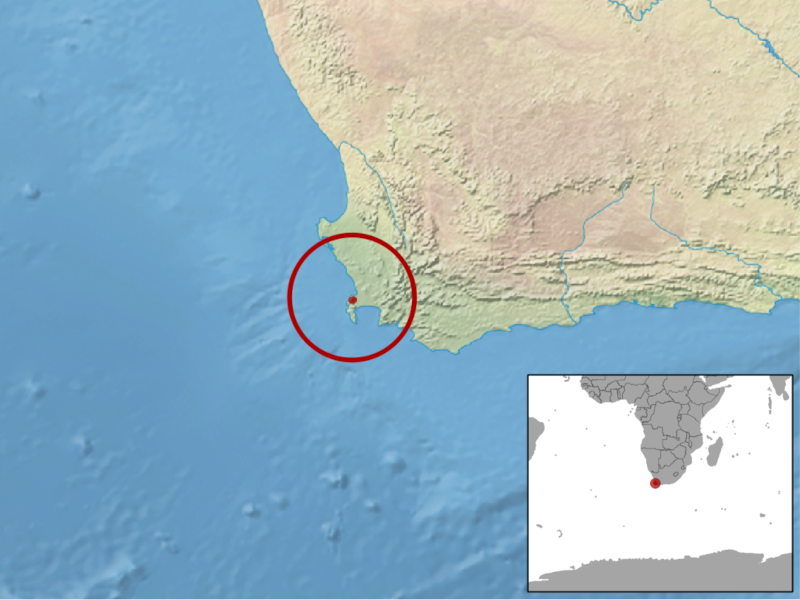
Rose’s Ghost Frog Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
Regrettably, the amazing Rose’s Ghost Frog evolved as native to an extremely limited region of the earth’s surface. The general area of that zone of habitation won’t surprise many people, though. That’s true since it developed as endemic to part of the continent of Africa.
Yet, inside of that greater section of the globe, this wonder appears in only an extremely restricted area. This mainly consists of the eastern and southern portions of one mountain. For the moment, a much smaller population also appears on the western slopes, as well.
The amphibian displays strong preferences for its choice of where to live. Situated on Table Mountain, in Cape Town, South Africa, its only known zone of habitation naturally plays a role in its habitat. It presently remains undetermined if it ever lived anywhere else.
It primarily appears in either of two ecosystems inside this area. One consists of moist, forested gorges, with stronly vertical stone sides. The other’s comprised of exposed streams, with relatively dense vegetation nearby. This usually appears at higher altitudes.
Like its many relatives, the Rose’s Ghost Frog evolved as carnivorous in nature. It feeds opportunistically, eating a wide range of locally prevalent insects and small arthropods. Its own predators currently remain undetermined, but likely include an array of local species.
The creature primarily remains concealed in cracks and under larger stones during the day. At night, it emerges to hunt. Breeding season begins in November, in response to a combination of environmental factors. It’s still unknown where females deposit their eggs.
Species Sharing Its Range


Bat Eared Fox

Check out our other articles on 4 Supremely Stunning Squirrels, Great Potoo, Great Barrier Reef, Red Maple, Moose, Australian Painted Lady, Fire Salamander, Alligator Snapping Turtle









Leave a Reply